

Population-based studies have demonstrated an overall prevalence rate ranging from 2.5% and 28%, with relatively increased rates attributable to incremental increases in age, and a gender predilection favoring DISH diagnosis in males compared to females. In an autopsy study, evidence of DISH was present in approximately one-fourth of the specimens, with a mean age of 65 years (minimum 50 years). Current postulations are that the disease course begins between the third and fifth decade of life but manifests clinically at a later age. These prevalence rates increase in patients over 80 years of age, with male and female prevalence rates of 28% and 26%, respectively. In the general population over 50 years of age, DISH occurs in about 25% of males, and 15% of females. The overall incidence in the general population is 6 to 12%. DISH is rarely reported in patients younger than 50 years of age. There have been relatively few publications regarding epidemiologic data for DISH. Furthermore, higher prevalence rates of aortic valve sclerosis have been previously identified as an independent risk factor predicting cardiovascular events in patients with DISH. For example, carotid atherosclerosis and DISH correlate at higher rates in patients with metabolic syndrome.
Further, angiogenesis remains a relatively popular investigative common denominator that, at least in theory, provides a feasible pathophysiologic linkage in various clinical manifestations of DISH. Some authors have attempted to describe underlying causes related to mechanical stress and strain patterns, exposure to various toxic factors, and genetic contributions.
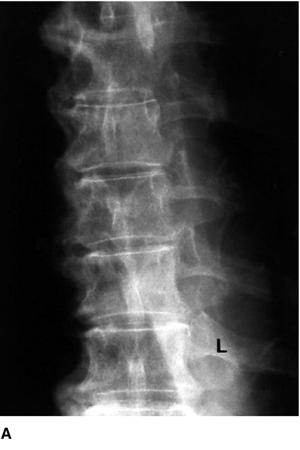
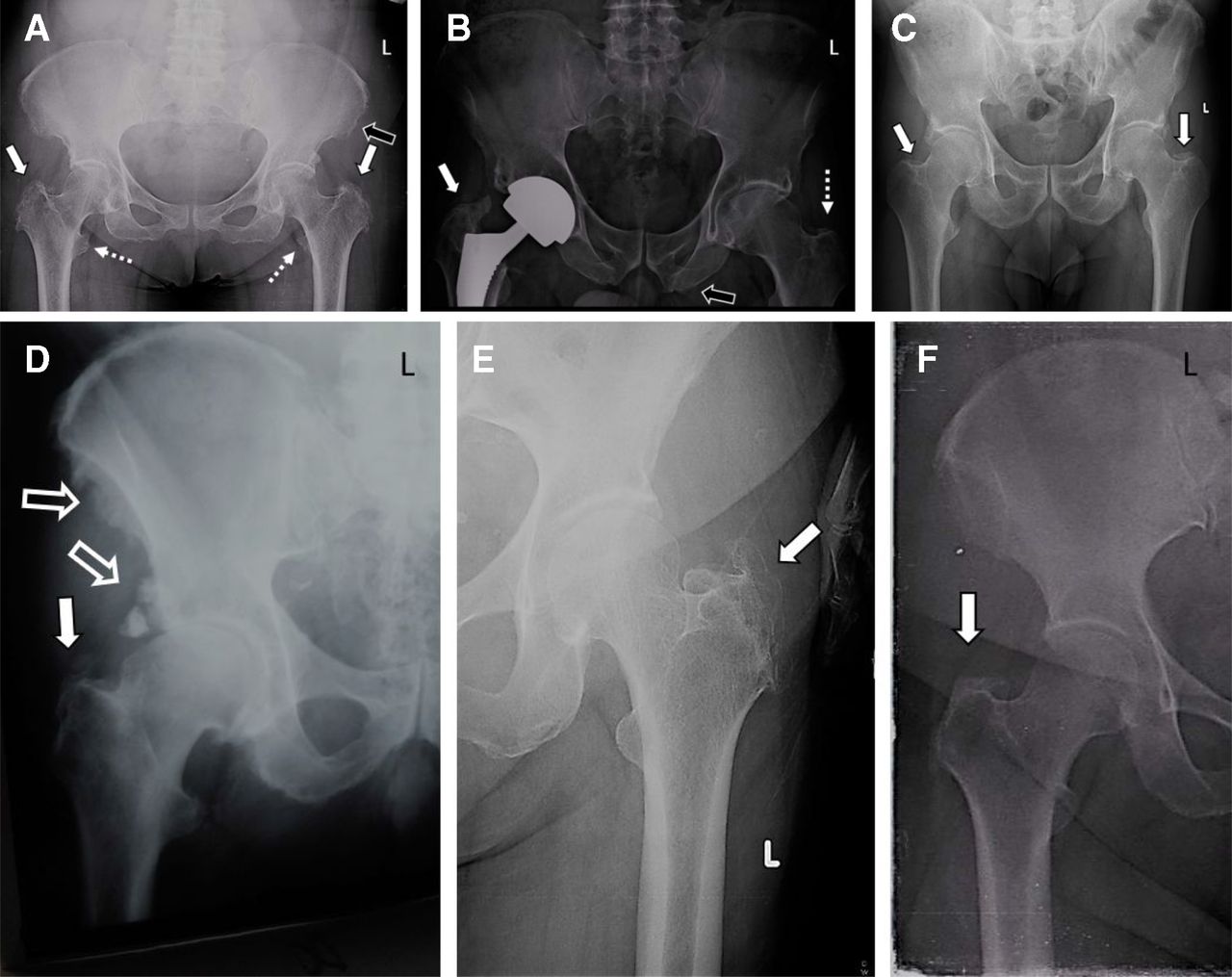
While these proposed clinical associations have been suggested in the literature, the pathogenesis and proposed mechanism contributing to these characteristic ossification patterns remain debatable. Several recent studies have revealed a significant association between DISH and metabolic disorders, such as diabetes mellitus, hyperinsulinemia, obesity, dyslipidemia, and hyperuricemia. Unlike other seronegative spondyloarthropathies, no apparent relationship has been identified between DISH and HLA-B27. As such, high rates of diabetes mellitus, hyperuricemia, and hyperlipidemia have been present in patients with DISH. HLA-B8 is common in both DISH and diabetes mellitus. While the etiology remains poorly defined, various risk factors have been identified in the literature, including gout, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes. DISH in the spine most commonly occurs on the right side of the thoracic spinal segment. Although less common, peripheral enthesopathy can occur at the shoulder, elbow, knee, or calcaneus. The ossifications are classically described in the spine as flowing ossifications along the anterolateral aspect in at least three successive vertebral levels or four contiguous vertebrae.
#Diptic diffuse idiopathic series#
Forestier and Rotes-Querol initially described the underlying pathology in specimens and a series of 200 patients in 1950, who called it “senile ankylosing hyperostosis.” The term is both inclusive and descriptive of the disorder. originally coined the term DISH in 1975 and is now the most commonly used term to describe this condition in the literature. DISH most commonly affects the spine and often presents as back pain and stiffness. This activity reviews the etiology, presentation, evaluation, and management of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and reviews the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating, diagnosing, and managing the condition.ĭiffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a systemic condition characterized by characteristic ossification patterns that can occur in the spine and peripheral entheses. Although less common, peripheral enthesopathy can occur at the shoulder, elbow, knee, or calcaneus. The ossifications are classically described in the spine as flowing ossifications along the anterolateral aspect in at least three successive vertebral levels or four contiguous vertebrae. DISH most commonly affects the spine and often presents as back pain and stiffness. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a systemic condition characterized by characteristic ossification patterns that can occur in the spine and peripheral entheses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
